
In the old EF6x world, I could use this command:Īdd-migration MyMigrationName -ignoreChanges So my problem in this instance was working with migrations against an existing database and model. Some things are not there or some of them are not feature complete.
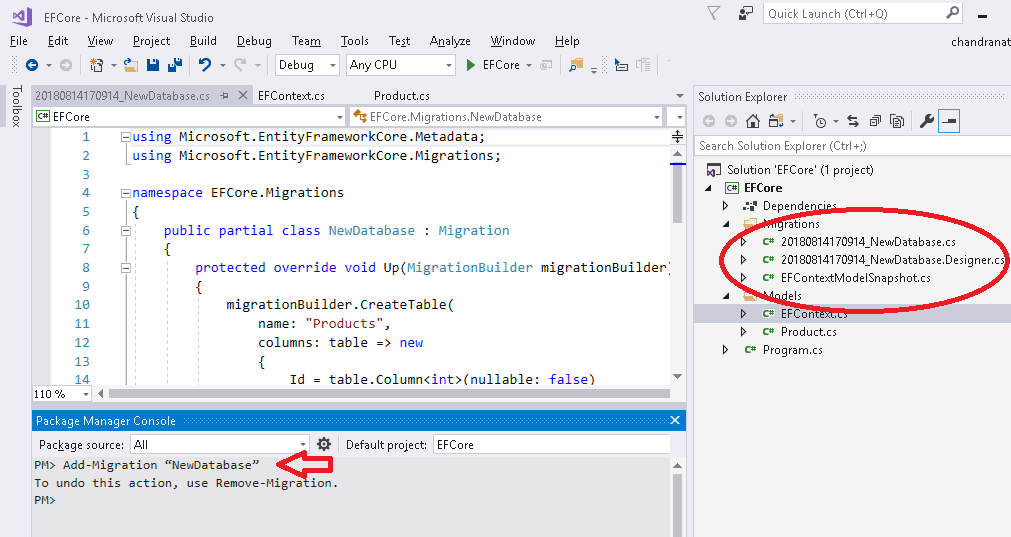
EF ADD MIGRATION COMMAND CODE
EF Core Code First is great but the tooling is still rough around the edges. The project also makes use of the newest ( " target="_blank) so it's all running on the edge of the. For now I'll leave it as it is but going forward I'll use the new format for subsequent ASP.NET Core projects. I'm still using the project.json project format instead of the newer *.csproj & msbuild one. NET Core project and I'm loving the experience. Then execute the following command.EF Core migrations with existing database schema and data 07 December 2016 Suppose you want to roll back the database schema to any of the previous states, then you can execute the update-database command with the –TargetMigration parameter to the point which you want to roll back to.įor example, suppose there are many migrations applied to the above SchoolDB database but you want to roll back to the first migration. Now, whenever you change the domain classes, execute Add-Migration with the name parameter to create a new migration file and then execute the Update-Database command to apply the changes to the database schema. To see the examples, type: "get-help Update-Database -examples".įor more information, type: "get-help Update-Database -detailed".įor technical information, type: "get-help Update-Database -full".Īt this point, the database will be created or updated. Updates the database to the current model by applying pending migrations. ConnectionString -ConnectionProviderName PM> get-help update-databaseĪpplies any pending migrations to the database. Use the –verbose option to view the SQL statements being applied to the target database.Įxecute the get-help update-database or get-help update-database -detailed command in PMC to know more about the command.
EF ADD MIGRATION COMMAND UPDATE
To see the examples, type: "get-help Add-Migration -examples".įor more information, type: "get-help Add-Migration -detailed".įor technical information, type: "get-help Add-Migration -full".Īfter creating a migration file using the add-migration command, you have to update the database.Įxecute the Update-Database command to create or modify a database schema. Scaffolds a new migration script and adds it to the project. Scaffolds a migration script for any pending model changes.Īdd-Migration To know more about add-migration command parameters, execute get-help add-migration or get-help add-migration -detailed commands in PMC, as shown below. This is the advantage over automated migration. You may also write your own custom code for additional configurations. The above command will create a _SchoolDB-v1.cs file with the Up() and Down() methods, as shown below.Īs you can see, the Up() method contains code for creating database objects and the Down() method contains code for dropping or deleting database objects. Now, you have to create a migration class using the Add-Migration command with the name of your migration class, as shown below. Protected override void OnModelCreating( DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) Public SchoolDBContext(): base( "SchoolDB")ĭatabase.SetInitializer( new MigrateDatabaseToLatestVersion()) Now, you need to set the database initializer MigrateDatabaseToLatestVersion in your context class, as shown below.
The Enable-Migrations command will create the Configuration class derived from DbMigrationsConfiguration with AutomaticMigrationsEnabled = false.

Open the Package Manager Console from Tools → Library Package Manager → Package Manager Console and then run the enable-migrations command (make sure that the default project is the project where your context class is). To use code-based migrations, first execute the enable-migrations command in the Package Manager Console. Update-Database: Executes the last migration file created by the Add-Migration command and applies changes to the database schema.
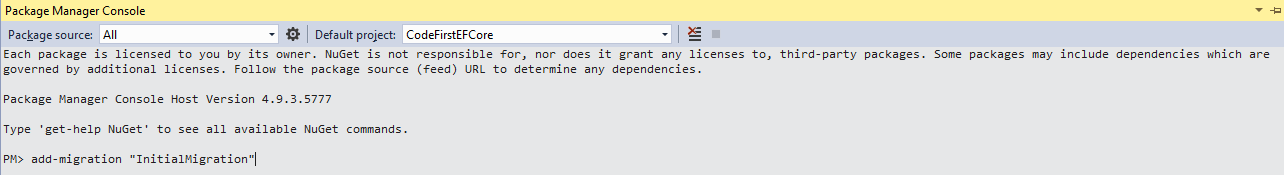
Add-Migration: Creates a new migration class as per specified name with the Up() and Down() methods.Enable-Migrations: Enables the migration in your project by creating a Configuration class.In order to use code-based migration, you need to execute the following commands in the Package Manager Console in Visual Studio: The code-based migration provides more control on the migration and allows you to configure additional things such as setting a default value of a column, configure a computed column etc.

Here, you will learn about code-based migration. In the previous chapter, you learned about automated migration which automatically updates the database schema when you change domain classes. Next Code-Based Migration in Entity Framework 6


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
